Representativity
The Devonian Period set the scene for many events that had a profound impact on the evolutionary history of life on Earth.
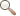 (40 kb) The animal and plant fossils of Miguasha date back 380 million years to the first half of the Frasnian Age (a division of the Upper Devonian), and represent many of the pivotal moments in the evolution of life. It was during the Devonian that...
(40 kb) The animal and plant fossils of Miguasha date back 380 million years to the first half of the Frasnian Age (a division of the Upper Devonian), and represent many of the pivotal moments in the evolution of life. It was during the Devonian that...

 (40 kb) The animal and plant fossils of Miguasha date back 380 million years to the first half of the Frasnian Age (a division of the Upper Devonian), and represent many of the pivotal moments in the evolution of life. It was during the Devonian that...
(40 kb) The animal and plant fossils of Miguasha date back 380 million years to the first half of the Frasnian Age (a division of the Upper Devonian), and represent many of the pivotal moments in the evolution of life. It was during the Devonian that...- The first forests formed, as witnessed by the numerous remains of Archaeopteris, the first known tree;
- The first seed plant appeared, and the megaspore Spermasporites
provides an insight on their origin.; - scorpions and myriapods were fossilized at Miguasha, providing valuable information about land-based invertebrate communities;
- anaspid and ostracoderm fish groups, both agnathans, became extinct, and their last representatives lived and died at Miguasha;
- placoderms (armoured fish) prospered, only to become extinct shortly after. One of them, Bothriolepis, is found at sites all over the world, but it is the Miguasha species, B. canadensis, that is the best described and serves as a reference for other species; the other placoderm, Plourdosteus, was like a smaller version of Dunkleosteus, the giant of the sea at the time;
- actinopterygians, the ray-finned fish that are so abundant today, began to really diversify. The species at Miguasha, Cheirolepis canadensis, serves as the primitive ancestral model for the group;
- the sarcopterygians at Miguasha attained a diversity unequalled elsewhere in the world, and some representatives, such as Eusthenopteron foordi, were at the root of lineages that eventually led to the first tetrapods;
- coelacanths made their first appearance; their most primitive representative is Miguashaia bureaui;
- dipnoan fish first appeared. Scaumenacia curta is one of the best known fossilized dipnoans;
- porolepiform fish appeared and then quickly disappeared. Two genera are present at Miguasha. One of them, Holoptychius, was particularly widespread and can also be found in Russia, Scotland, Belgium, New Brunswick, Pennsylvania, etc.
- elpistostegalian fish made a furtive appearance and then became extinct, but only after giving rise to the first tetrapods. At the heart of this exclusive group are Elpistostege from Miguasha, Panderichthys from Greenland, and Tiktaalik from Canada’s Far North.
Site map | Feedback | Links | Sources | Credits
Representativity
<< A window through time | Fossil quality >>

Title: The Miguasha paleoestuary
Author: Illustration by François Miville-Deschênes
Sources: Parc national de Miguasha
Year: 2003
Description:
A fresco of the ancient Miguasha estuary with the peaks of the young Appalachian mountain range in the background. The fish fauna were diversified, but it was Eusthenopteron foordi that dominated this watery world. Vegetation was concentrated along the shore, dense and tall enough in places to make forests.