The birth of the Appalachians
How is it possible that fossilized sea animals, fish included, are found at the heart of the Chic Choc mountains in the Gaspé hinterland? The answer is that these fossils are dramatic proof the Earth’s surface underwent major changes in the distant past.
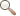 (112 kb) The fossil-bearing sedimentary rocks of the Gaspé region were deposited in an ancient marine environment before powerful forces raised them up from the watery depths to their present elevation. Fossiliferous marine sediments are even found high up on the world’s tallest mountain – Mount Everest in the Himalayas!
(112 kb) The fossil-bearing sedimentary rocks of the Gaspé region were deposited in an ancient marine environment before powerful forces raised them up from the watery depths to their present elevation. Fossiliferous marine sediments are even found high up on the world’s tallest mountain – Mount Everest in the Himalayas!
The birth of the Appalachians, and that of many other mountain chains, is caused by the movement of continental plates. When two plates collide, they push against each other and the resulting pressure buckles the crust or forces one plate beneath the other, uplifting the land and giving rise to a mountain chain.
The Appalachians were created in this manner when ancient continental masses collided. For a period of 150 million years, the part of Laurentia that now corresponds to northeastern North America gradually approached the continent of Baltica, present-day northwestern Europe, until they collided. The seafloor between them and any sediments being deposited along the ocean margins were folded and uplifted to form the Gaspesian segment of the Appalachians.

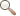 (112 kb) The fossil-bearing sedimentary rocks of the Gaspé region were deposited in an ancient marine environment before powerful forces raised them up from the watery depths to their present elevation. Fossiliferous marine sediments are even found high up on the world’s tallest mountain – Mount Everest in the Himalayas!
(112 kb) The fossil-bearing sedimentary rocks of the Gaspé region were deposited in an ancient marine environment before powerful forces raised them up from the watery depths to their present elevation. Fossiliferous marine sediments are even found high up on the world’s tallest mountain – Mount Everest in the Himalayas!The birth of the Appalachians, and that of many other mountain chains, is caused by the movement of continental plates. When two plates collide, they push against each other and the resulting pressure buckles the crust or forces one plate beneath the other, uplifting the land and giving rise to a mountain chain.
The Appalachians were created in this manner when ancient continental masses collided. For a period of 150 million years, the part of Laurentia that now corresponds to northeastern North America gradually approached the continent of Baltica, present-day northwestern Europe, until they collided. The seafloor between them and any sediments being deposited along the ocean margins were folded and uplifted to form the Gaspesian segment of the Appalachians.
Site map | Feedback | Links | Sources | Credits
The birth of the Appalachians
<< The closing of an ocean | A sea of fossils >>